
Content
What is Compliance?
The term “Compliance” refers to the set of procedures, standards and practices that organizations adopt to identify, assess and manage legal and operational risks. The main objective of Compliance is to establish effective internal mechanisms that prevent, control and respond to risk situations that may compromise the stability and continuity of the organization.
Today, compliance has evolved from a voluntary option to an essential requirement for many companies, due to the expansion of the global legal framework and the increase in regulatory rigor. This proactive and preventive approach not only ensures compliance with legal obligations, but also protects the company against sanctions and damage to its reputation.
Although the concept of Compliance is not new, its importance has grown considerably due to the tightening of sanctions and the evolution of international legislation. Current regulations highlight the need to implement preventive measures to ensure compliance, positioning Compliance as a fundamental tool in modern business management.
Compliance, also known as regulatory compliance, essentially seeks to implement programs that promote respect for laws and regulations. Its function is to prevent irregular behavior both within the organization and by its employees, thus avoiding criminal liability for the legal entity.
Furthermore, with the growing relevance of intangible assets, such as intellectual property and brands, Compliance extends to the management and protection of these assets. Implementing an effective Compliance program also involves ensuring that companies adequately record and protect their intangibles, which translates into added value for the organization.
What Are Intangible Assets?
Intangible assets are those resources that do not have a physical form but that provide significant value to a company. Unlike tangible assets, such as machinery or buildings, intangibles focus on aspects such as intellectual property, reputation and business relationships.
Among the most common types of intangible assets are:
- Intellectual property:Includes patents, trademarks, copyrights and trade secrets. These assets protect innovations and creations, allowing companies to gain a competitive advantage.
- GoodwillGoodwill: Refers to the value a company has built through its reputation, customer loyalty, and business relationships. Goodwill is especially relevant in mergers and acquisitions, where the value of the brand can outweigh the value of tangible assets.
- Licenses and FranchisesThese agreements allow companies to operate under a recognized brand or use specific technologies, generating additional revenue and expanding their market reach.
- Customer Relations: Customer loyalty and satisfaction are intangible assets that can be difficult to measure, but are essential to the growth and sustainability of a business.
- Organizational Capabilities: They include the knowledge, experience and skills of staff, which contribute to operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Proper management and protection of intangible assets is vital to maximizing their value. Implementing a Compliance framework helps companies comply with regulations related to intellectual property and establish policies that promote their correct use and protection, thus ensuring their preservation and contributing to the long-term success of the organization.
Importance of Intangible Assets for Businesses
Intangible assets are essential for the growth and competitiveness of companies in today's environment. The following are some of the most prominent reasons for their importance:
- Competitive Advantage: Intangible assets, such as intellectual property and goodwill, can provide companies with a significant advantage in the marketplace. Constant innovation and brand recognition help differentiate them from the competition.
- Business ValuationIn many cases, the value of a company goes beyond its tangible assets. During mergers and acquisitions, intangible assets are essential in determining the purchase price, as they reflect the company's ability to generate future revenue.
- Customer LoyaltyStrong customer relationships, built through trust and satisfaction, are a vital intangible asset. A loyal customer base not only ensures recurring revenue, but also facilitates expansion and growth into new markets.
- Flexibility and Adaptation: Companies that possess intangibles such as knowledge and experience are more agile in their ability to adapt to changes in the market. Innovation and continuous improvement are driven by human capital and organizational culture.
- Legal Protection and MonetizationIntangible assets, such as patents and trademarks, offer legal protection against unauthorized use and can be monetized through licensing or franchise agreements, generating additional revenue.
- Reputation and Credibility: A good reputation in the market translates into trust from customers, suppliers and investors. Reputation, as an intangible asset, can be a decisive factor in purchasing decisions and in the general perception of the company.
- Talent Development: Investing in staff training and development contributes to creating a positive and productive work environment. Human capital is a critical intangible asset that drives innovation and improves operational efficiency.
- Impact on Stock Market Valuation: For publicly traded companies, intangible assets can influence their valuation. Investors often consider factors such as innovation, brand and reputation when evaluating a company's growth potential.
Compliance Objectives
The main purpose of implementing a Compliance program is to align corporate objectives with legal requirements at both national and international levels. This involves regulating the company's internal operations so that they comply with the standards and codes designed to ensure such compliance.
Compliance is a dynamic function that must constantly adapt to an expanding and increasingly complex regulatory framework. To meet these challenges, compliance management systems are structured around three fundamental pillars:
- Prevention
In this phase, the goal is to equip the company with the necessary tools to prevent the commission of crimes. Procedures are established to ensure legal compliance, integrating them into the daily behavior of employees. Key tasks in this phase include:- Identification and assessment of risks, often through compliance audits.
- Design and implementation of protocols and procedures, including a mandatory internal reporting channel.
- Guidance and support to the different areas of the company.
- Promoting an ethical tone from senior management and board members.
- Awareness and training of the entire organization.
- Development of hiring and promotion policies.
- Detection and Reporting
In this phase, potential breaches are identified and the responsible body is informed so that it can take appropriate action. This phase is crucial as the company can be held liable for offences committed due to the omission of its supervision, monitoring and control duties. The company can be exempted from liability if it demonstrates that it has implemented effective monitoring and control measures. Activities in this phase include:- Monitoring and controlling compliance with the prevention model.
- Communication of findings to the Board of Directors.
- Measurement and evaluation of the performance of the Compliance system.
- Resolution
In the event of non-compliance, corporate compliance is responsible for mitigating or compensating the impact of improper actions. To do so, the following must be done:- Establish recommendations and measures to resolve incidents, correct deficiencies and prevent their recurrence.
- Apply sanctions in accordance with the established disciplinary system.
- Review and adjust the Compliance model to correct detected errors or adapt to changes in the company or in regulations.
What is the Compliance process in a company?
The process of compliance It is usually divided into several stages, and can vary depending on the type of organization and the jurisdiction in which it operates, but generally includes the following steps:
1. Risk assessment
Before implementing a compliance program, the organization must conduct a risk assessment. This involves identifying, analyzing and classifying the potential risks that the company could face in terms of compliance, such as:
- Legal risks (violation of local or international laws).
- Financial risks (fraud, money laundering, tax evasion).
- Operational risks (non-compliance with internal or external regulations).
- Reputational risks (loss of trust due to questionable practices).
2. Compliance program design
Based on the risk assessment, the company must design an appropriate compliance program. This includes:
- Clear policies and procedures to prevent, detect and correct unethical or illegal conduct.
- Appointment of a compliance officer (compliance officer) to oversee the program and ensure its implementation.
- Establishment of internal control mechanisms that ensure compliance with regulations.
3. Training and awareness raising
It is essential that all employees are informed and trained on the policies and regulations of the compliance program. Training should cover:
- Applicable laws and regulations.
- The internal policies of the organization.
- Procedures for reporting violations in a secure and confidential manner.
- Practical cases to help employees recognize risk situations.
4. Continuous monitoring and auditing
Once the compliance program is in place, the company must continuously monitor its effectiveness. This includes:
- Regular audits to verify that internal controls are working.
- Constant review of policies and procedures to adapt them to legal or market changes.
- Monitoring suspicious activities that may suggest non-compliance with regulations.
5. Incident investigation and management
When a potential breach or irregularity is detected, the company must have an investigation protocol. This includes:
- Assess the severity of the incident.
- Determine responsibilities and take corrective actions.
- Implement disciplinary or legal measures if necessary.
- Review and modify policies to prevent future incidents.
6. Reporting and accountability
It is important for the company to maintain a transparency on its compliance activities, both internally and towards its stakeholders (shareholders, regulatory authorities, customers, etc.). This may include:
- Regular reporting to senior management on the status of compliance.
- Reporting to the relevant authorities when necessary (for example, in case of serious violations).
- Review the effectiveness of the program through key performance indicators (KPIs).
7. Continuous improvement
The compliance process must be dynamic, meaning it must constantly evolve and adapt. Continuous improvement can be achieved by:
- Incorporating lessons learned from previous incidents.
- The integration of new technologies or practices that improve the effectiveness of the program.
- Adaptation to regulatory or market changes.
Why is Compliance and the registration of intangibles necessary in companies?
The legislative environment in which companies operate has evolved towards greater complexity and rigor. Increased scrutiny by authorities and regulatory bodies has intensified the impact of regulations, especially in critical areas such as registration and protection of intangibles.
With the rise of corporate scandals and a growing interest in business ethics, both public and private organizations are adopting ethical and legal standards as an essential part of their good governance protocols. Complying with these standards is not optional; it has become a strategic imperative.
The risks faced by companies include reputational damage, severe financial penalties and the potential loss of contracts, which can limit business opportunities. In the realm of intangibles, failure to properly register and protect assets such as trademarks, patents and copyrights can result in the loss of significant value.
Complying with legal obligations regarding intangibles should not be seen as a mere administrative formality. A proactive approach to compliance management enables not only ongoing compliance, but also the identification of opportunities to maximize the value of intangible assets and improve the company's competitive position. By thoroughly understanding the regulations governing their sector and intangibles management, companies can avoid risks and capitalize on strategic advantages in an increasingly competitive market.
What is needed to register an intangible in compliance terms?
In order to register an intangible asset for compliance purposes, it is necessary to comply with several legal, administrative and internal management requirements. This ensures that the asset is registered correctly and that the organization is protected against possible infringements.
- Asset Identification and Documentation
- Detailed Description: Create a complete description of the intangible asset, including its nature (brand, patent, copyright, etc.), its function, and how it adds value to the company.
- Evidence of Creation or Acquisition: Documenting in detail how the asset was created or acquired. This may include acquisition contracts, development documents, or proofs of originality to demonstrate ownership of the asset.
- Search and Verification of Pre-Existing Rights
- Pre-Existing Rights Analysis: Conducting a pre-existing rights investigation to confirm that the asset does not infringe third party rights. This is crucial for patents, trademarks and copyrights, where a thorough search of intellectual property records must be conducted.
- Avoid Infringements: Compare the property with other similar records to avoid the risk of infringement and possible legal sanctions.
- Compliance with Regulations and Registration Procedures
- Comply with Registration Rules: Follow the specific procedures of the relevant regulatory body (e.g., patent and trademark office, copyright office, or software registration office).
- Format and Registration Requirements: Ensure that the documentation submitted complies with the formats and formal requirements required by the regulatory body, including specific forms, registration fees and deadlines.
- Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
- Licenses and Rights of Use: Check whether additional licenses are required to exploit the intangible asset or whether there are restrictions on use.
- Third-Party Contracts: If the asset was developed in collaboration with third parties or under contract, it must be verified that the contracts correctly transfer property rights to the company.
- Internal Audit and Document Control
- Property Audit: Conduct a thorough internal audit to validate that all documentation related to property assets is complete, up-to-date, and properly organized. This audit should ensure that property titles, contracts, permits, records, and any other relevant documents are in compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
- File Maintenance: Implement a secure and accessible filing system to store all documentation related to property assets. Files should include, in an orderly and classified manner, title deeds, contracts, registration applications, certificates and any other relevant supporting documents. In addition, adequate protection measures should be ensured to prevent loss or unauthorized access to confidential information.
- Statement of Book Value
- Accounting Valuation: Perform an accurate accounting valuation of intangible assets, using recognized methods and criteria in accordance with international accounting standards (such as IFRS or GAAP). This valuation must faithfully reflect the current value of the intangible asset and be adequately documented for presentation in the company's financial statements.
- Tax Declaration: Ensure that the valuation and accounting of intangible assets comply with local tax and regulatory provisions. This includes verifying that the corresponding tax deductions or amortizations are applied correctly, in accordance with current tax legislation, to optimize the tax burden and ensure compliance with tax obligations.
- Protection Plan and Compliance Strategy
- Protection Policies: Implement internal policies that define how the asset will be protected, who has access to it, and what measures will be taken if violations are detected.
- Monitoring and Active Surveillance: Establish monitoring systems to identify potential rights violations and have a rapid response plan in case of misuse of the asset.
- Compliance Training and Awareness
- Staff Training: Ensure that the team is trained to manage and protect intangible assets, understanding the importance of intellectual property and potential legal implications.
- Compliance Culture: Promote a culture of compliance in the organization so that all employees understand the importance of protecting and respecting the company's intangible assets.
- Update and Renewal
- Renewals and Extensions of Rights: For assets that require renewals (e.g. trademarks), keep track of expiration and renewal dates to avoid loss of rights.
- Monitoring Changes in Legislation: Stay abreast of changes in intellectual property legal regulations that may affect the status or management of the asset.
- Legal Documentation and Specialized Advice
- Legal Advice: Obtain advice from lawyers or intellectual property experts to ensure that all requirements are met when registering and maintaining the asset.
- Confidentiality and Non-Competition Agreements: For intangible assets that involve confidential information, it is advisable to have confidentiality agreements (NDAs) with employees and partners.
What benefits does the implementation of Compliance bring to SMEs?
- Boosting Business Growth: Ensuring compliance reinforces the trust of customers, employees and suppliers in your company. This trust increases the reputation of the organization, thus facilitating business growth and expansion of the customer base.
- Legal Risk Reduction: Compliance minimizes the risk of facing fines, penalties, labor disputes, lawsuits, or even company closure. While noncompliance can result in warnings and opportunities to correct failures, in other cases, it can lead to significant penalties. Taking proactive compliance measures helps avoid these problems and protect the legal stability of the company.
- Improved Operations and Safety: Implementing rules on discrimination and harassment contributes to a healthier work environment, which can result in increased productivity. In addition, adhering to safety regulations prevents workplace accidents, fires and emergency situations, which protects the company's profitability and operational continuity.
- Strengthening the Corporate Image: Complying with legal obligations offers the opportunity to highlight these achievements on your website and marketing materials. For example, when posting job advertisements, you can highlight that your company promotes equal opportunities. Additionally, when recruiting new employees, you can underline your commitment to safety and well-being by mentioning policies such as extended maternity and paternity leave.
How to implement Compliance in a company or SME?
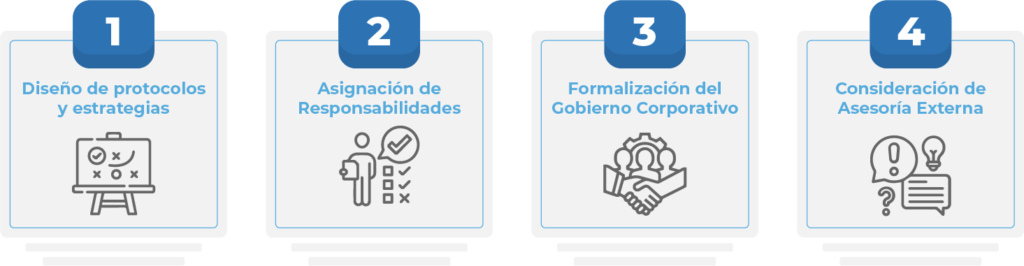
To effectively develop and implement a Compliance Plan, a number of essential steps must be followed to ensure the creation of a robust and effective system. These steps include:
- Design of Protocols and Strategies
- Establishment of Protocols: Create detailed procedures for the identification, prevention and management of legal and operational risks.
- Strategy Development: Define clear strategies for risk detection and implementation of preventive measures.
- Review and Update: Conduct periodic reviews of the plan to ensure its effectiveness and adapt it to new regulations and emerging situations.
- Assignment of Responsibilities
- Appointment of a Compliance Officer: Designate a professional or team in charge of ensuring regulatory compliance and supervising the Compliance Plan.
- Establishment of Communication Channels: Implement internal communication and reporting channels to facilitate the prevention and reporting of potential crimes or breaches.
- Formalization of Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance Structure: Clearly define the corporate governance structure and ensure that all members of the organization understand and adhere to the Compliance policy.
- Policy Communication: Ensure that Compliance policies and procedures are known by all levels of the company, from senior management to operational staff.
- Consideration of External Advice
- Hiring of Experts: If the company lacks the necessary infrastructure or personnel, it is advisable to hire an external consultancy with experience in Compliance. These experts can provide the necessary support to implement and maintain an effective compliance system.
Types of Compliance in the Company
When implementing Compliance in a company, two main types of models can be distinguished: generic and specific. Each addresses different aspects of regulatory compliance depending on the context and needs of the organization.
- Generic Models
- Compliance Superstructure Model: Based on the global regulatory framework, this model follows the ISO 19600 standard, which provides guidelines and good practices for establishing a comprehensive Compliance function in any company or organization. This approach ensures that the Compliance system covers the basic principles of governance and risk management, applicable to any sector.
- Specific Models
Specific models focus on specific legal areas, tailored to the particular needs of each organization. These include:- Criminal Compliance: Focused on crime prevention and compliance with criminal law. Includes measures to prevent illegal activities and manage criminal risks.
- Corporate Compliance: Addresses compliance with general and specific regulations affecting corporate structure and operations, such as corporate laws and internal regulations.
- Environmental Compliance: It focuses on compliance with environmental regulations and management of environmental impacts, promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
- Occupational Risk Prevention Compliance: Aimed at complying with occupational health and safety legislation, ensuring a safe and healthy work environment.
- Anti-Corruption Compliance: Focused on preventing acts of corruption and bribery, promoting transparency and integrity in all business transactions.
- Public Health Compliance: It focuses on complying with public health regulations, ensuring that business operations do not put the health of the community at risk.
- Fiscal and Tax Compliance: Addresses compliance with fiscal and tax obligations, ensuring that the company complies with tax and tax laws.
The Relationship between Compliance and the Registry of Intangibles
Compliance plays a crucial role in the management and protection of a company's intangible assets, such as brands, patents and copyrights. An effective Compliance framework not only ensures compliance with legal regulations related to the registration and protection of these assets, but also promotes ethical and responsible practices in their management.
Proper registration of intangibles is essential to secure intellectual property rights and prevent infringements. A robust compliance program helps companies establish clear procedures to identify, register and protect these assets, minimizing the risk of litigation and sanctions. It also fosters the creation of an organizational culture that values innovation and respect for intellectual property rights.
By implementing compliance policies, companies can ensure that all employees understand the importance of protecting intangibles and comply with relevant regulations. This not only protects the company's assets, but also enhances its reputation in the market and contributes to its long-term sustainability. In a business environment where intangibles represent a significant part of an organization's total value, the intersection between compliance and intangibles registration becomes essential for strategic success.
Compliance in Mexico: Legal Aspects and Regulations Applicable to Companies
In recent years, the concept of compliance has gained increasing importance in Mexico, moving from being a voluntary practice to becoming a legal requirement in various circumstances. Today, various regulations and legislative provisions require companies to implement compliance programs to ensure that their operations comply with legality and ethical standards.
- Securities Market Law: Article 19, Section I, establishes the obligation for publicly traded companies to have a compliance program that allows them to prevent illegal practices, such as money laundering or financing of terrorism. This requirement is essential to ensure transparency in the securities market and protect investors.
- Federal Attorney for Environmental Protection (PROFEPA): It has been recognized that an effective compliance program can serve as proof of the non-repetition of environmental crimes. In this sense, companies that implement policies and practices aligned with environmental legislation can obtain benefits in the event of violations, such as reduced penalties or exemption from liability for repeat offenses.
- Federal Penal Code: The reformed regulatory framework has introduced the Special Procedure for Legal Entities, which allows compliance programs to play a key role in the investigation, prosecution and sanctioning of companies that commit crimes. This procedure allows not only the application of sanctions to those directly responsible for a crime, but also the imputation of criminal liability to the legal entities themselves, promoting greater corporate responsibility.
The Mexican legal framework has evolved to incorporate compliance as an essential tool for the proper functioning of companies, particularly those operating in regulated sectors or those that are exposed to high risks of non-compliance. Companies that implement and maintain robust compliance programs not only minimize their exposure to legal risks, but also improve their reputation and their ability to operate in an ethical and responsible manner.
Compliance and Reportable Schemes
What are Reportable Schemes?
The reportable schemes These are tax or financial structures that must be reported to the competent authorities due to their potential to evade taxes or abuse tax rules. These schemes are often complex and may involve tactics designed to exploit legal loopholes or avoid tax obligations. The obligation to report these schemes helps authorities identify practices that could be harmful to the tax system and take the necessary measures to counteract them.
The Relationship between Compliance and Reportable Schemes
The intersection between compliance and reportable schemes lies in the commitment of organizations to ethical and compliant conduct. Here are two key ways in which they are related:
Prevention and Detection: A robust compliance program includes mechanisms for detecting and reporting tax or financial schemes that may be considered evasive. By integrating specific procedures to identify these schemes within the compliance framework, organizations not only ensure compliance with the law, but also act proactively to avoid future problems.
Regulatory Compliance: Reportable scheme regulations often require firms and their advisors to report certain structures or transactions. Incorporating these requirements into the compliance program ensures that the firm is not only aware of legal obligations, but also has the mechanisms in place to properly comply with them. This involves having clear processes for scheme assessment, staff training, and reporting to the relevant authorities.
Integrating reportable schemes into a company’s compliance framework strengthens the organization’s ability to operate within legal and ethical boundaries. It is not just about complying with laws, but about taking a proactive stance in managing risks and promoting transparent and responsible business practices. In an increasingly complex regulatory environment, this relationship not only protects the company, but also reinforces its commitment to integrity and long-term sustainability.



