Transfer Pricing

content structure
Transfer pricing is the adjustment of the price of goods and services sold between related or controlled legal entities within a company, for example, if a subsidiary company sells goods to a parent company, The cost of those goods paid by the parent company to the subsidiary is the transfer price.

What are the advantages of transfer pricing?
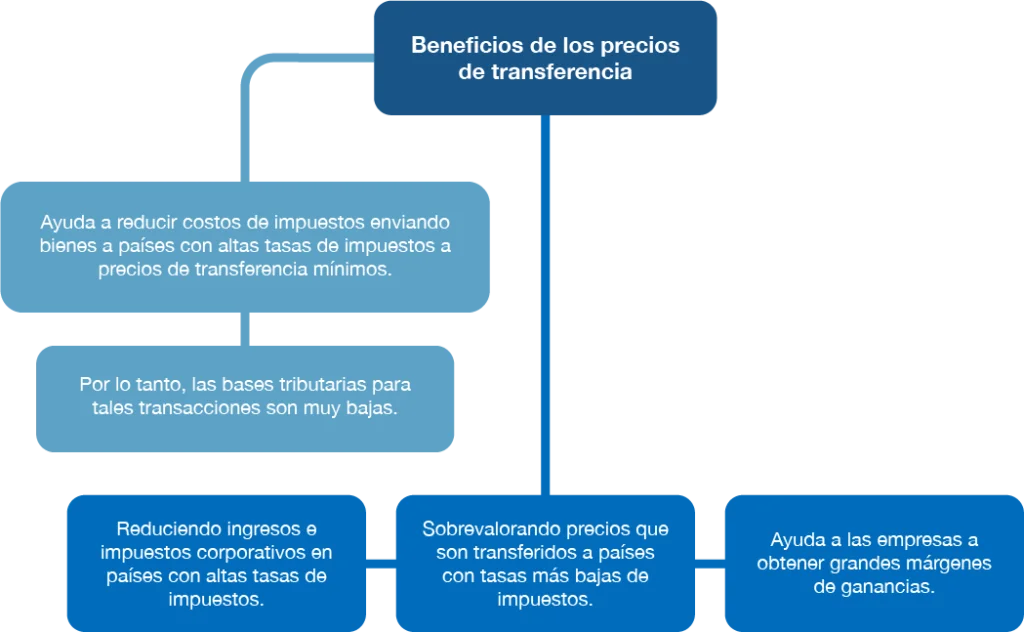
Transfer pricing has tax-related advantages, companies may have book profits from goods and services in different countries that have lower tax rates, in some cases, the transfer of goods and services from one country to another within transactions of interrelated companies may allow a company to evade tariffs on internationally traded goods and services. This is not well seen by the regulatory authorities.
International tax laws are governed by the OECD (Organization for Economic Development and Cooperation)
What is the principle of free competition?
Article 9 of the Tax Convention of the OECD establishes that transfer prices between two mutually controlled entities must be treated as if they were two independent entities.
The principle of free competition is based on real markets and provides an international standard of inspection, which allows governments to collect their share of taxes. and at the same time prevent transnational companies from paying double contributions.
What benefits do transfer pricing have?
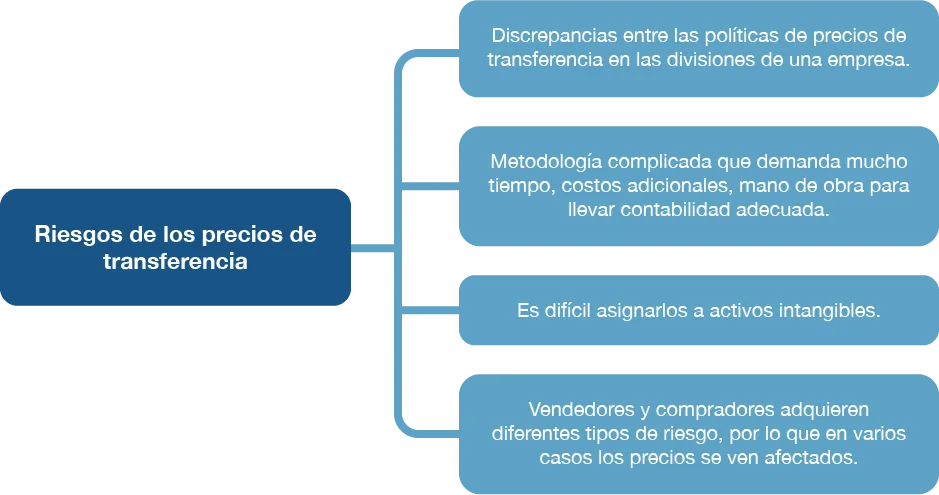
What risks do transfer pricing have?
A company must determine the monetary value of goods and services and treat that value as sales revenue to the selling unit and as a cost to the buying unit.
Transfer Pricing Example
The ACER company, which is dedicated to the manufacture of mice for computing equipment, manufactures them at a cost of 10 pesos in Mexico; its subsidiary company ACER ELECTRONICS located in Brazil, it sells the mouse to the public at a price of 50 Mexican pesos and spends 10 Mexican pesos to distribute and advertise them.
So the company's total profit per mouse is 30 Mexican pesos. ACER decides to assign a transfer price of between 10 and 30 pesos to its subsidiary ACER ELECTRONICS and will seek where the tax rates are lower to move its profits there. If the tax charges are higher in Mexico than in Brazil, it will assign the lower transfer price in Brazil to sell the mice and thus benefit from the lower tax charge than in Mexico.
How important is the transfer pricing study?
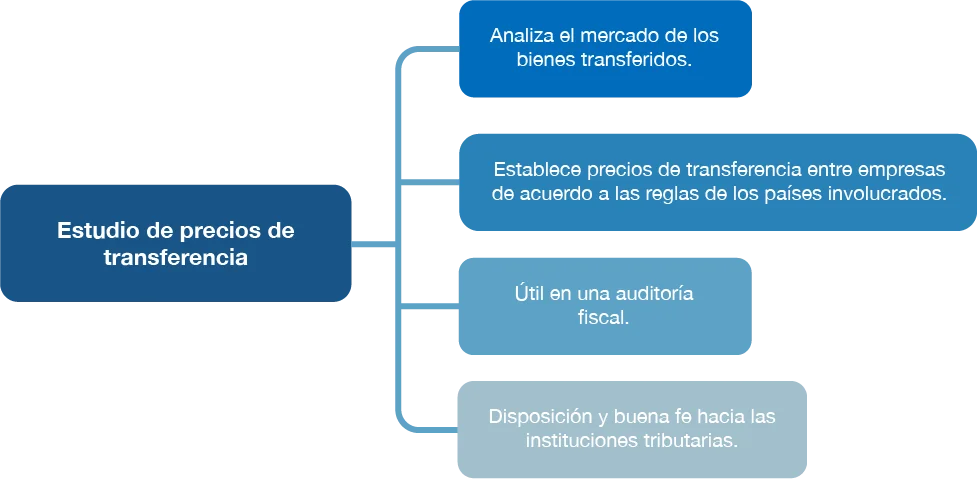
They are of vital importance since it helps us to maintain control when making transfers between related companies, since thus it is impossible for false prices to be given in order to benefit your business group and that are not in line with market values.
The CNR publishes financial statements for tax purposes that must be declared as part of the tax return of the tax authorities if the taxpayer complies with its obligations for transfer fees, Therefore, it is important to always have transfer pricing management in good condition.
Just like it is a tool that allows monitoring operations at the level of a group of companies, to develop corporate strategies in order to optimize resources and decision making.
What types of declarations are made?
- Master statement:
This obligation gives an overview of multinational groups in relation to their businesses, this in order to help tax administrations to measure the presence of risks.
After Action 13 is incorporated into the Income Tax Law (LISR) with the purpose of avoiding the attrition of the tax base and transfer of profits, this declaration must have global information of the group and the possibility of presenting it by each business line. All information must always be available to the relevant authorities.
- Local statement:
For this declaration, it is necessary for the company to detail the information of its specific operations within the group to assure the authorities that the taxpayer has complied with the principle of full competition (arm's length) for its intra-group operations carried out with national and foreign related parties. . Its proper functioning will provide certainty to the organization and will avoid possible complications in its relationship with the tax authorities.
- Country-by-country statement:
This declaration format also called CBCR, for its acronym in English, needs specific information such as; the allocation of income, taxes paid, as well as indicators of economic activity between the tax jurisdictions where a multinational company is present. The correct use of this statement helps companies not to fall into a scenario of double taxation.
- Supply chain analysis:
The goal is to develop a well-functioning chain in which tax matters are integrated as a part of the entire business process. With a thorough understanding of tax burden and transfer pricing regulation, significant resource savings can be achieved in the long run. With the help of qualified third-party consulting, a business can create economies of scale, operational efficiencies, and positively influence customer service, thus achieving supply chain optimization.
- Transfer pricing implementation in practice:
The correct implementation of the transfer pricing policy involves three main aspects: processes, technology and personnel. They should be considered to strengthen the activities related to this topic. In this way, it is possible to integrate this practice into daily operations, align execution with strategy, and improve the accuracy of intercompany records. Implementation is a cycle that involves planning a strategy to ensure proper compliance with the policy and documentation.
If you are interested in learning more about these topics, follow us In all our social networks, we have content that may interest you.

IN MEMORY OF
Francisco Xavier Garcia NavaMechanical Engineer / Appraiser